Table of Contents
Financial investment business spend money on part of their customers who, in return, share in the revenues and losses.
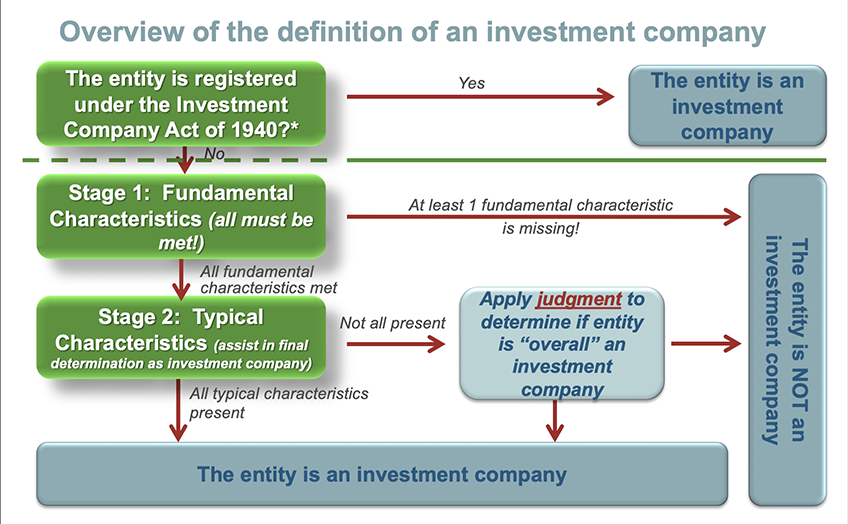
Financial investment companies do not include brokerage firm companies, insurance coverage business, or banks.
A significant type of business not covered under the Financial Investment Firm Act 1940 is exclusive investment firm, which are merely private firms that make financial investments in stocks or bonds, but are restricted to under 250 capitalists and are not controlled by the SEC. These funds are often made up of really wealthy investors.
This offers specific protections and oversight for investors. Regulated funds normally have constraints on the types and amounts of financial investments the fund supervisor can make. Usually, controlled funds may just purchase noted protections and no greater than 5% of the fund might be purchased a single safety and security. The bulk of investment companies are common funds, both in terms of variety of funds and assets under administration.
Mineral Rights Companies
The first investment counts on were developed in Europe in the late 1700s by a Dutch investor that wanted to allow small capitalists to merge their funds and diversify. This is where the idea of investment firm stem, as stated by K. Geert Rouwenhorst. In the 1800s in England, "investment merging" arised with trusts that appeared like modern financial investment funds in structure.
The 1929 stock exchange accident and Wonderful Clinical depression temporarily interfered with investment funds. Brand-new safeties laws in the 1930s like the 1933 Stocks Act restored financier self-confidence. A number of developments then brought about stable development in investment company possessions and accounts over the years. The Investment Firm Act of 1940 controls the framework and procedures of investment firm.
In 1938, it accredited the creation of self-regulatory organizations like FINRA to supervise broker-dealers. The Securities Act of 1933 requires public protections offerings, including of investment company shares, to be signed up. It also mandates that capitalists receive an existing program describing the fund. "Investment firm". United State Stocks and Exchange Commission (SEC).
Investment Company
Lemke, Lins and Smith, Law of Investment Firm, 4.01 (Matthew Bender, 2016 ed.). Chaudhry, Sayan; Kulkarni, Chinmay (2021-06-28). "Layout Patterns of Spending Applications and Their Results on Spending Behaviors". ACM. pp. 777788. doi:10.1145/ 3461778.3462008. ISBN 978-1-4503-8476-6. "Investment Clubs and the SEC",, Changed January 16, 2013. (PDF). Financial Investment Company Institute. 2023.
In retail mutual fund, thousands of capitalists may be involved via middlemans, and they may have little or no control of the fund's activities or understanding about the identities of various other capitalists. The prospective number of financiers in a private financial investment fund is normally smaller sized than retail funds. Personal mutual fund often tend to target high-net-worth people, including politically exposed individuals, and fund supervisors may have a close connection with their customer investors.

Passive funds have been growing in their market share, and in some jurisdictions they hold a substantial section of ownership in openly traded business. There are several categories for mutual fund. Some are closed-end, indicating they have a fixed number of shares or capital, whilst others are open-end, implying they can grow right into limitless shares or resources.
The pricing, risk, and regards to by-products are based on a hidden possession, and they allow capitalists to hedge a position, increase leverage, or speculate on a property's change in value. For example, a capitalist could own both a stock and a choice on the exact same supply that allows them to market it at an established rate; for that reason, if the supply's price drops, the alternative still retains value, lowering the capitalist's losses.
Whilst taken into consideration, provided the focus of this rundown on the crawler of business vehicles, a complete treatment of the advantageous possession of possessions is outside its range. A financial investment fund acts as a conduit to gain from several assets being held as investments. Investors can be individuals, corporate vehicles, or organizations, and there are usually a number of intermediaries between the investor and mutual fund in addition to in between the mutual fund and the underlying economic properties, particularly if the fund's systems are exchange-traded (Box 1).
Investment Company in Bryan, Texas
Relying on its lawful form and framework, the people working out control of an investment fund itself can differ from the individuals that own and profit from the underlying properties being held by the fund at any kind of provided moment, either directly or indirectly. Both retail and private mutual fund usually have fund supervisors or consultants who make investment choices for the fund, picking safeties that line up with the fund's goals and take the chance of tolerance.
and serve as intermediaries in between investors and the fund, facilitating the trading of fund shares. They connect financiers with the fund's shares and carry out professions on their part. manage the enrollment and transfer of fund shares, keeping a document of investors, refining ownership adjustments, and releasing proxy products for shareholder meetings.
Navigation
Latest Posts
Landscape Designer
Landscape Design Services
Mineral Rights Companies in Bryan